What is PLA?
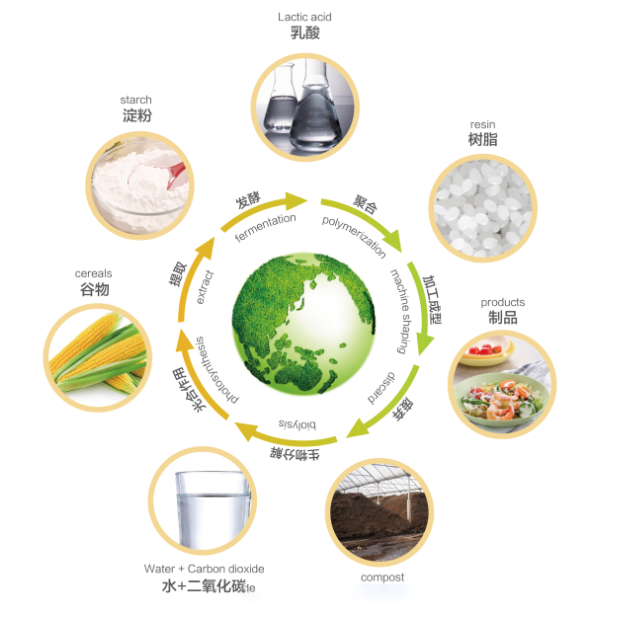
Polylactic acid, also known as PLA (Polylactic Acid), is a thermoplastic monomer derived from renewable organic sources such as corn starch or sugarcane or beet pulp.
Although it is the same as previous plastics, its properties have become renewable resources, making it a more natural alternative to fossil fuels.
PLA is still carbon neutral, edible, and biodegradable, which means it can completely decompose in appropriate environments instead of breaking into harmful microplastics.
Due to its ability to decompose, it is commonly used as a packaging material for biodegradable plastic bags, straws, cups, plates, and tableware.
Degradation mechanism of PLA
PLA undergoes non biological degradation through three mechanisms:
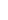
Hydrolysis: The ester groups in the main chain are broken, resulting in a decrease in molecular weight.
Thermal decomposition: a complex phenomenon that results in the formation of different compounds, such as lighter molecules, linear and cyclic oligomers with different molecular weights, and lactide.
Photodegradation: Ultraviolet radiation can cause degradation. This is the main factor that exposes polylactic acid to sunlight in plastic, packaging containers, and film applications.
The hydrolysis reaction is:
-COO- + H 2 O → -COOH + -OH
The degradation rate is very slow at ambient temperature. A 2017 study found that PLA did not experience any quality loss within a year in seawater at 25 ° C (77 ° F), but the study did not measure the decomposition or water absorption of polymer chains.
What are the application areas of PLA?
1. Consumer goods
PLA is used in various consumer goods, such as disposable tableware, supermarket shopping bags, kitchen appliance casings, as well as laptops and handheld devices.
2. Agriculture
PLA is used in fiber form for single fiber fishing lines and nets for vegetation and weed control. Used for sandbags, flower pots, binding straps, and ropes.
3. Medical treatment
PLA can be degraded into harmless lactic acid, making it suitable for use as medical equipment in the form of anchors, screws, plates, pins, rods, and nets.
The four most common possible scrapping situations
1. Recycling:
It can be chemical recycling or mechanical recycling. In Belgium, Galaxy has launched the first pilot plant for chemical recycling of PLA (Loopla). Unlike mechanical recycling, waste may contain various pollutants. Polylactic acid can be chemically recovered as monomers through thermal polymerization or hydrolysis. After purification, the monomers can be used to manufacture raw PLA without losing their original properties.
2. Composting:
PLA can be biodegraded under industrial composting conditions, first through chemical hydrolysis, then through microbial digestion, and finally degraded. Under industrial composting conditions (58 ° C (136 ° F)), PLA can partially (about half) decompose into water and carbon dioxide within 60 days, with the remaining portion decomposing much slower thereafter, depending on the crystallinity of the material. In an environment without necessary conditions, decomposition will be very slow, similar to non biological plastics, which will not completely decompose for hundreds or thousands of years.
3. Burning:
PLA can be incinerated without producing chlorine containing chemicals or heavy metals, as it only contains carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms. Burning scrapped PLA will generate 19.5 MJ/kg (8368 btu/lb) of energy without leaving any residue. This result, along with other findings, indicates that incineration is an environmentally friendly method for treating waste polylactic acid.
4. Landfill:
Although PLA can enter landfills, it is the least environmentally friendly choice because the material degrades slowly at ambient temperatures, typically as slowly as other non degradable plastics.
Post time: Nov-20-2024